Comparison of Satellite-Based Soil Moisture
Estimates
and Rainfall Data for a New Mexico Watershed
Background Study Area
Data
Methods
Results &
Conclusions
Soil Moisture Data
Soil moisture data
were obtained from the Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) mission onboard a
NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) satellite (https://smap.jpl.nasa.gov/). Measurements are based on natural microwave
emissions recorded by a radiometer. SMAP data is gridded with a spatial
resolution of 81 km2 and a temporal resolution 11-37 hours. Figure 2
shows 31 soil moisture estimates for the month of August 2018.
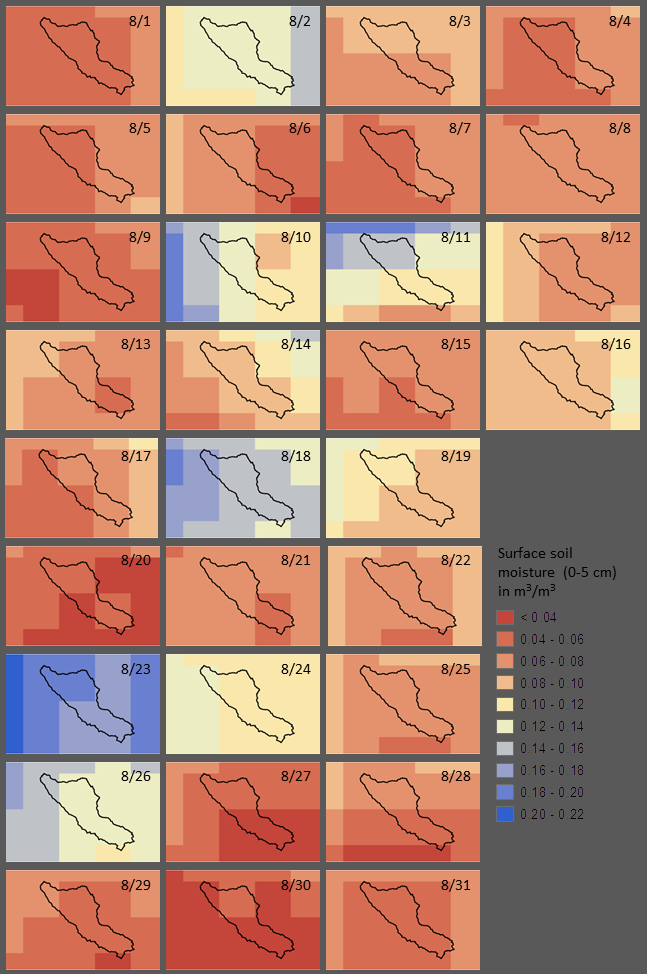
Figure 2:
SMAP soil moisture estimates for the study area, August 1-31, 2018 (dates based
on UTC).
Precipitation Data
Rainfall
data were obtained from nine tipping bucket rain gages (Figure 3, yellow
circles) and Next-Generation Radar (NEXRAD) Quantitative Precipitation
Estimation (QPE) products (https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/data-access/radar-data/nexrad).
Gage data represent point measurements of precipitation in 0.01 inch (0.254 mm)
increments with a temporal resolution of 5 minutes. Radar derived rainfall
estimates are gridded, whereby grid resolution decreases with distance from the
radar tower. Temporal resolution of radar data ranges from 4-15 minutes.
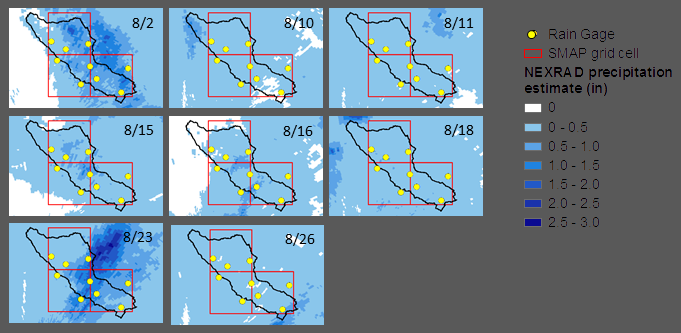
Figure 3:
NEXRAD precipitation accumulation for eight storms in the study area during
August 2018 (dates based on UTC).