 |
||||||||
 |
||||||||
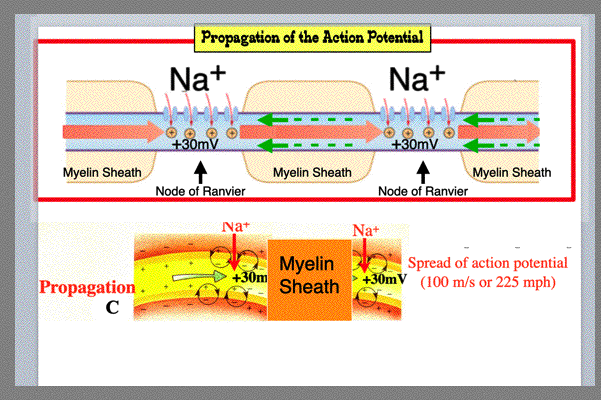
| CLASS: BE ABLE TO DRAW and LABEL (West Point Technique) the Action Potential! Explanations for Each Step of the Action Potential: a) RESTING MEMBRANE POTENTIAL (RMP): RMP at -70mV. Na+ on outside and K+ on inside of cell b) DEPOLARIZATION: As depolarization reaches THRESHOLD of -55mV, the action potential is triggered (opening the voltage regulate Na+ gates) and Na+ rushes into cell. Membrane potential reaches +30mV on action potential c) PROPAGATION: Propagation (which means spreading or moving) of the action potential at 100 m/sec (which is 225 mph). Membrane potential at +30mV d) REPOLARIZATION: Repolarization occurs with K+ exiting the cell to return to -70mV (i.e., the cell restores itself to RMP) e) NA+/K+ PUMP: Return of ions (Na+ and K+) to their extracellular (Na+) and intracellular (K+) sites by the sodium potassium (Na+/K+) pump NOTE: An Action Potential is a substantial depolarization. At homeostasis, the cell is continuosly alternating from positive (depoloarization) and negative (hyperpolarization) charges. When the cell attains threshold (-55mV), the action potential occurs. CLASS: BE ABLE TO DRAW and LABEL the Action Potential for the Exam |
||||||||
 |
||||||||
| With the propagation of the action potential, note how the 'spread' of the message travels from Node of Ranvier to the next Node of Ranvier. The positive charge of the Na+ ions rushing in draws negative charges towards it. This causes the membrane to reach threshold (-55mV) and for the voltage-regulated gates to open and the depolarization of the membrane to +30mV. This propagation continues along the axon to its axon terminal. | ||||||||
|