|
|
 |
||||||||
 |
||||||||
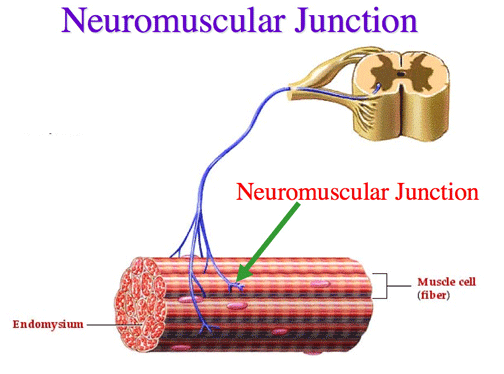
| Arrival of the Action Potential at the Neuromuscular junction | ||||||||
| Impulse (action potential) arrives at axon terminal | ||||||||
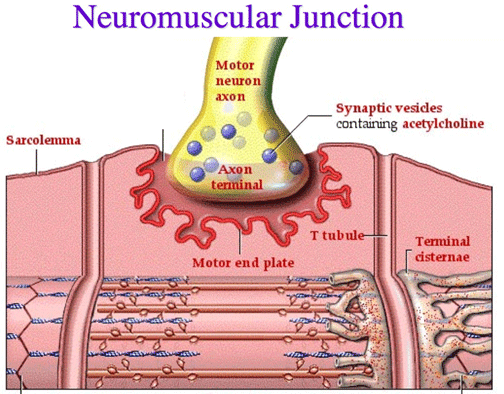
| Ca++ ions rush in (as action potential activated Ca++ gates); Ca++ reacts with synaptic vesicles | ||||||||
| Synaptic vesicles fuse with cell membrane of axon terminal | ||||||||
| ACh (acetylcholine) released through a process known as exocytosis | ||||||||
| ACh binds with motor end plate receptors: deplorization occurs as Na+ rushes into the muscle cell | ||||||||
| Impulse travels through T-tubules which excite the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) | ||||||||
| Ca++ ions release from the SR | ||||||||
| Ca++ binds with troponin | ||||||||
| Shift of tropomyosin, which makes the binding sites available for myosin S1 units to bind | ||||||||
| With ATP present, ATPase splits (hyrolysis) ATP to ADP and Pi and Energy | ||||||||
| Myosin S1 units can now bind to active sites on actin | ||||||||
| Sliding action of actin over myosin called the Power Stroke | ||||||||
| Impulse stops to muscle; calcium ions pumped back into SR by active transport (energy requiring) pumps | ||||||||
| Tropomyosin returns over the active sites on actin and muscle action ceases | ||||||||
| STUDENTS, PLEASE GO TO THIS LINK BELOW AND SCROLL DOWN TO CHALLENGE YOURSELF WITH A PRACTICE QUIZ ON THE SEQUENCE OF MUSCLE CONTRACTION | ||||||||
| http://www.unm.edu/~lkravitz/Exercise%20Phys/muscle.html | ||||||||
|
||||||||